Water is essential for your health, but not all water is safe to drink. You might wonder how dirty or harmful water becomes clean and safe.
The answer lies in a simple process: the three steps of water purification. Understanding these steps can help you protect yourself and your family from waterborne illnesses. Keep reading to discover how water transforms from unsafe to safe, and learn how you can ensure your water is pure every time.
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Water Collection
Water collection is the first step in water purification. It means gathering water from natural or man-made sources. Clean water collection is very important for safe drinking water.
Collecting water carefully helps remove dirt and germs early. This makes the next purification steps easier and more effective.
Sources Of Water
Water comes from many different places. It is important to know where water is collected to keep it clean.
- Rivers and streams
- Lakes and ponds
- Rainwater
- Groundwater from wells
- Stored water in tanks or reservoirs
Each source has different risks and needs different care during collection. For example, river water may have more dirt than rainwater.
Importance Of Clean Collection
Collecting water cleanly stops dirt and germs from entering. This helps protect your health and saves time in cleaning water later.
Dirty collection points can cause water to have bacteria and harmful chemicals. Clean collection keeps water safe for drinking and cooking.
- Use clean containers to collect water
- Cover water storage to avoid dust and bugs
- Collect water away from waste or pollution
- Clean collection areas regularly

Credit: www.freepik.com
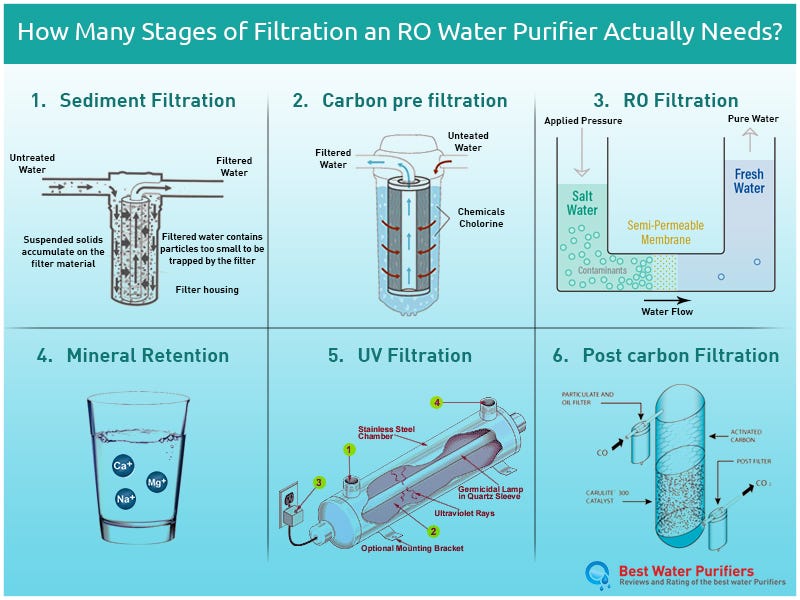
Filtration Process
The filtration process is a key step in water purification. It removes dirt, particles, and some harmful substances from water.
This step helps make water clearer and safer to use. It usually happens before other purification steps.
Types Of Filters
Filters come in different types based on how they clean water. Each type targets certain impurities.
Common filters include sand filters, activated carbon filters, and membrane filters.
- Sand filters:Use layers of sand to trap large particles.
- Activated carbon filters:Remove odors and chemicals by adsorption.
- Membrane filters:Use tiny pores to block bacteria and small particles.
Removing Particles And Sediments
Particles and sediments in water include dirt, sand, and rust. These can make water look dirty.
Filtration traps these solids by passing water through layers of filter material.
- Water flows through filter layers.
- Large particles get caught first.
- Smaller particles are trapped in deeper layers.
- Clean water passes through the filter.
Disinfection Methods
Disinfection is a vital step in water purification. It kills harmful germs and makes water safe to drink.
There are several ways to disinfect water. Each method uses a different process to remove bacteria and viruses.
Chlorination
Chlorination adds chlorine to water to kill germs. It is one of the most common disinfection methods.
Chlorine works by breaking down the cell walls of bacteria and viruses. This stops them from growing and spreading.
- Easy to use and low cost
- Effective against many germs
- Leaves a small chlorine taste
- Needs careful dosing to be safe
Uv Treatment
UV treatment uses ultraviolet light to kill germs in water. It stops bacteria and viruses from multiplying.
This method works fast and does not change the water’s taste or smell. It is good for clear water.
- Does not use chemicals
- Kills many types of germs
- Needs electricity to work
- Water must be clear for best results
Boiling
Boiling water is one of the oldest ways to disinfect it. Boiling kills germs by heat.
Water should boil for at least one minute to be safe. This method works without any chemicals or tools.
- Simple and effective
- No need for special equipment
- Uses fuel or electricity
- Does not remove dirt or chemicals
Credit: what-am-i-drinking.fandom.com
Common Contaminants
Water purification removes harmful substances from water. These substances are called contaminants. They make water unsafe to drink.
Contaminants include living things and chemicals. They can cause illness or damage to the body. Knowing about these helps in cleaning water properly.
Biological Pollutants
Biological pollutants are tiny living things in water. They include bacteria, viruses, and parasites. These can cause diseases like diarrhea and cholera.
Water purification removes these pollutants by killing or filtering them out. Boiling and using filters are common ways to remove biological pollutants.
- Bacteria: Salmonella, E. coli
- Viruses: Hepatitis A, Norovirus
- Parasites: Giardia, Cryptosporidium
Chemical Pollutants
Chemical pollutants are harmful substances from factories, farms, or natural sources. They include pesticides, heavy metals, and chlorine. These chemicals can harm organs and cause long-term illness.
Water purification removes these pollutants by using chemicals or special filters. Activated carbon filters are effective in removing many chemical pollutants.
- Pesticides: Insecticides, herbicides
- Heavy metals: Lead, mercury, arsenic
- Disinfectants: Chlorine, chloramine
Maintaining Purified Water
Water purification removes harmful substances from water. Keeping water clean after purification is important. Proper care helps keep water safe to drink.
This section explains how to store purified water correctly and test it regularly to maintain its quality.
Storage Tips
Store purified water in clean, food-grade containers. Avoid containers that can leak chemicals or break easily.
Keep water containers in a cool, dark place. Sunlight and heat can cause bacteria to grow and spoil the water.
- Use sealed containers to prevent contamination
- Label containers with the date of purification
- Do not store water near chemicals or strong smells
- Clean containers before refilling with purified water
Regular Testing
Check purified water often to ensure it stays clean and safe. Testing helps find any problems early.
Use simple water test kits to check for bacteria, chemicals, and other impurities. Test water every few weeks if stored for a long time.
- Test for bacteria to avoid illness
- Check pH levels for water balance
- Look for cloudiness or strange smells
- Replace water if tests show contamination
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Three Main Steps Of Water Purification?
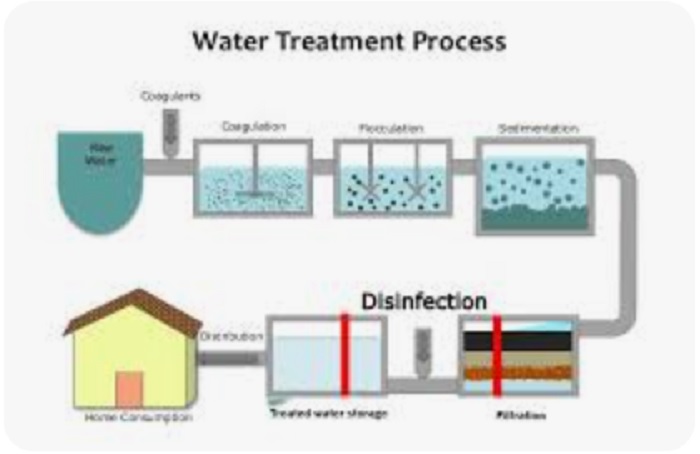
The three main steps of water purification are coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration. Coagulation involves adding chemicals to form clumps. Sedimentation allows these clumps to settle. Finally, filtration removes remaining particles, ensuring clean and safe water for consumption.
How Does Coagulation And Flocculation Work?
Coagulation and flocculation involve adding chemicals to water to form clumps of impurities. These clumps, known as flocs, are easier to remove. The process helps in clearing the water by making particles larger and heavier, allowing them to settle during sedimentation.
What Happens During Sedimentation In Water Purification?
During sedimentation, water is left undisturbed, allowing heavier flocs to settle at the bottom. This process separates the solids from the clear water. Sedimentation is a crucial step as it significantly reduces the amount of suspended particles in the water.
Why Is Filtration Important In Water Purification?
Filtration is essential as it removes remaining particles from water after sedimentation. It involves passing water through filters made of sand, gravel, or membranes. This step ensures that even the smallest impurities and microorganisms are removed, making the water safe to drink.
Conclusion
Water purification involves three simple steps: filtration, sedimentation, and disinfection. Each step plays a key role in making water safe to drink. Filtration removes large particles. Sedimentation lets smaller dirt settle down. Disinfection kills harmful germs. Following these steps helps protect your health.
Clean water means fewer illnesses. Everyone deserves safe water every day. Understanding these steps makes you more aware. Keep water pure for a healthy life. It’s a small effort with big benefits.