Water is the source of life, and clean water is essential for your health and well-being. But have you ever stopped to think about where your water comes from and how it stays pure?
At the same time, the soil beneath your feet plays a crucial role in growing the food you eat and supporting the environment. Yet, soil erosion threatens this balance, leading to serious problems that could affect your daily life. Understanding the important areas of water purification and soil erosion control is not just for experts—it’s something that impacts you directly.
Keep reading to discover how these processes work and why paying attention to them can make a real difference for you and your community.

Credit: www.mdpi.com
Water Purification Methods
Clean water is important for health and the environment. Water purification removes harmful substances and makes water safe to use.
There are many ways to purify water. These methods use physical, chemical, and biological processes. Some use new technologies to improve results.
Physical Filtration Techniques
Physical filtration removes particles from water by passing it through materials. These materials trap dirt and debris.
Common filters include sand, gravel, and cloth. They help clean water by blocking solid waste.
- Sedimentation: lets heavy particles settle down
- Sand filtration: uses sand layers to remove particles
- Membrane filtration: filters water through tiny holes
- Screening: removes large debris with mesh screens
Chemical Treatment Processes
Chemical treatment adds substances to water to kill germs or remove pollutants. It helps stop waterborne diseases.
Chlorine and ozone are common chemicals used. They destroy bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microbes.
- Chlorination: adds chlorine to kill germs
- Ozonation: uses ozone gas for disinfection
- Coagulation: adds chemicals to clump particles
- pH adjustment: balances water acidity or alkalinity
Biological Purification Approaches
Biological methods use living organisms to clean water. These organisms break down harmful substances.
Natural wetlands and biofilters help remove pollutants. These systems support bacteria that eat waste.
- Constructed wetlands: use plants and microbes
- Biofiltration: filters water through microbe layers
- Activated sludge: uses bacteria to digest waste
- Bioremediation: cleans water using microbes
Advanced Technologies In Water Purification
New technologies improve water purification. They make cleaning faster and more effective.
Techniques like UV light and reverse osmosis remove tiny impurities and germs. These methods support clean water goals.
- Ultraviolet (UV) treatment: uses UV rays to kill microbes
- Reverse osmosis: filters water through a special membrane
- Nanofiltration: removes very small particles and chemicals
- Electrodialysis: uses electric current to separate salts

Credit: www.mdpi.com
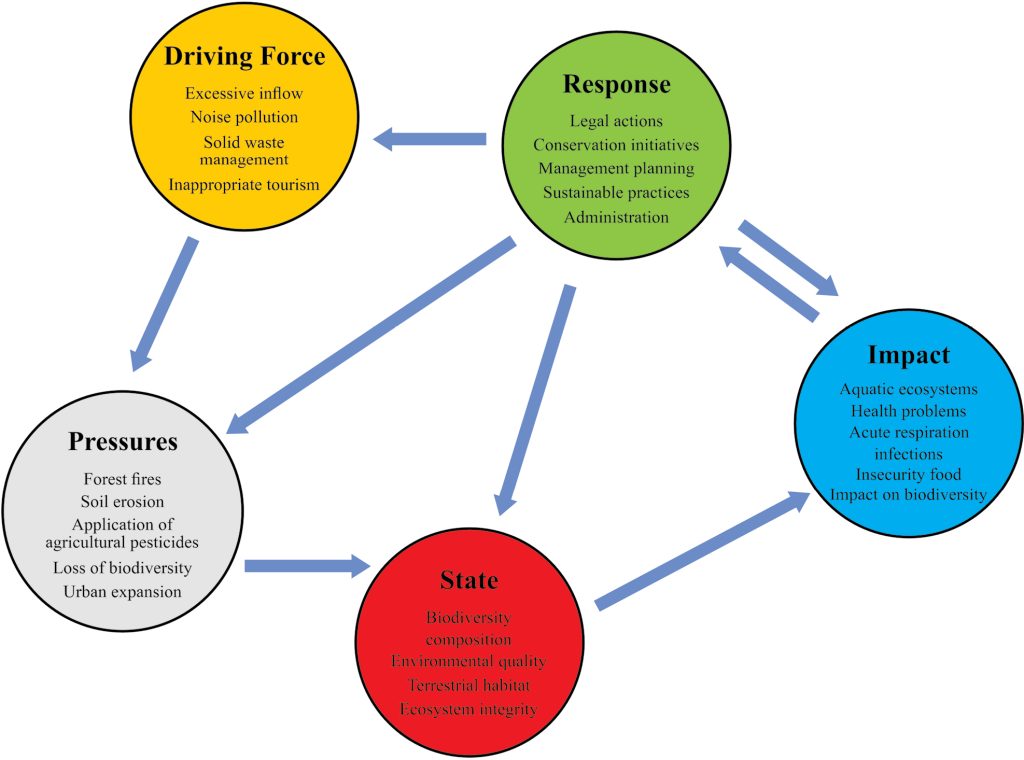
Sources Of Water Contamination
Water contamination is a big problem for the environment and health. It happens when harmful substances enter water bodies like rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
Knowing where pollution comes from helps us protect water and soil. These sources include industrial waste, farming, city pollution, and natural causes.
Industrial Waste Impact
Factories release chemicals and heavy metals into water. These wastes can poison fish and plants. They also harm people who drink or use the water.
Industrial waste often contains toxic substances like lead, mercury, and acids. These can change water quality and make it unsafe.
- Discharges from factories and plants
- Oil spills and chemical leaks
- Heavy metals and toxic chemicals
- Heat pollution affecting aquatic life
Agricultural Runoff Effects
Rain can wash fertilizers and pesticides from farms into water. These chemicals cause water pollution and harm fish and plants.
Soil erosion from farms adds dirt and nutrients to water. This can cause algae growth, which lowers oxygen for fish.
- Fertilizers with nitrogen and phosphorus
- Pesticides and herbicides
- Animal waste from farms
- Soil particles from erosion
Urban Pollution Challenges
Cities produce a lot of pollution that drains into water. Oil, trash, and chemicals from streets harm water quality.
Stormwater carries pollutants like plastic, heavy metals, and chemicals into rivers and lakes. This affects drinking water and wildlife.
- Oil and grease from cars and roads
- Trash and plastic waste
- Heavy metals from construction sites
- Cleaning chemicals and detergents
Natural Contaminants
Some water pollution comes from nature. Minerals and organic materials can enter water from soil and rocks.
Natural contaminants include bacteria, viruses, and dissolved salts. These can affect water taste and safety.
- Minerals like arsenic and fluoride
- Natural organic matter
- Bacteria and viruses from wildlife
- Saltwater intrusion in coastal areas
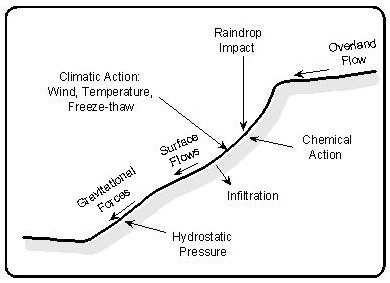
Soil Erosion Causes
Soil erosion happens when the topsoil washes or blows away. This loss harms plants and crops. It also affects water quality and land stability.
Many human activities and natural forces cause soil erosion. Understanding these causes helps us protect the land better.
Deforestation Consequences
Cutting down trees removes roots that hold soil in place. Without roots, soil becomes loose and easy to wash away. Deforestation leads to faster erosion and land damage.
Clear-cut areas also lose shade. This makes soil dry and weak. Rain then carries the soil downhill, causing more problems.
Agricultural Practices
Farming can cause soil erosion if not done carefully. Plowing fields leaves soil exposed to wind and rain. Overgrazing by animals removes grass that protects soil.
Using heavy machines can compact soil and reduce its strength. Poor crop rotation also weakens soil, making it easier to erode.
Water And Wind Erosion
Water erosion happens when heavy rain or floods wash soil away. It can create deep ditches and damage land. Wind erosion blows loose soil away, especially in dry areas.
- Water erosion causes gullies and sediment in rivers
- Wind erosion removes fine soil and dusts the air
- Both reduce soil quality for farming and plants
Urban Development Impact
Building roads and houses removes natural soil cover. Construction dirt often washes into nearby areas. This increases erosion and pollutes water.
Urban areas also change water flow. Rainwater moves faster on paved surfaces, carrying soil away. This causes erosion in new places.
Techniques For Soil Erosion Control
Soil erosion is a major problem that harms land and water quality. Using different techniques helps keep soil in place and protects the environment.
These techniques reduce soil loss, improve water absorption, and support plant growth. They are important for farming, landscaping, and land management.
Vegetative Cover And Planting
Plants hold soil with their roots and slow down water flow. Vegetative cover includes grass, shrubs, and trees that protect soil from wind and rain.
Planting crops or cover plants after harvest keeps the soil safe during off-seasons. This also adds nutrients back to the soil.
- Grasses reduce surface runoff
- Trees prevent strong wind erosion
- Cover crops improve soil health
Terracing And Contour Plowing
Terracing shapes land into steps to slow water flow on slopes. This reduces soil washing away and helps water soak into the ground.
Contour plowing means plowing along the land’s curves. This creates natural barriers that stop water from running straight downhill.
- Terraces reduce slope length
- Contour plowing follows land shape
- Both reduce water speed and erosion
Use Of Mulches And Geotextiles
Mulches are materials spread on soil to protect it. They keep soil moist, reduce rain impact, and stop weeds from growing.
Geotextiles are fabric sheets placed on soil to hold it in place. They allow water to pass but stop soil from moving.
- Organic mulches include straw and wood chips
- Inorganic mulches include plastic films
- Geotextiles are strong and long-lasting
Engineering Structures
Engineering structures are built to control water flow and support soil. Examples are check dams, retaining walls, and drainage channels.
These structures slow water, trap soil, and stop landslides. They work well on steep slopes and areas with heavy rain.
- Check dams reduce water speed in streams
- Retaining walls hold back soil on slopes
- Drainage channels guide water safely away
Integrated Solutions For Water And Soil
Water purification and soil erosion control are key for a healthy environment. Combining efforts helps protect natural resources.
Integrated solutions improve water quality and prevent soil loss. This supports farming, wildlife, and clean water supplies.
Sustainable Land Management
Sustainable land management uses farming and land care methods that keep soil healthy. It limits erosion and improves water use.
Techniques include crop rotation, cover crops, and no-till farming. These protect soil and help water soak into the ground.
- Planting trees and vegetation to hold soil
- Using terraces on slopes to reduce runoff
- Maintaining soil cover with mulch or plants
- Reducing heavy machinery that compacts soil
Community Involvement And Education
Communities play a big role in protecting water and soil. Education helps people understand their impact on the environment.
Local groups can organize cleanups and plant trees. Teaching children about nature encourages care for land and water.
- Workshops on soil and water care
- Community tree planting events
- School programs about pollution and erosion
- Sharing tips on reducing waste and runoff
Policy And Regulatory Measures
Rules and policies help protect water and soil on a large scale. They set limits on pollution and land use.
Government programs support farmers and landowners who use safe practices. Laws require treatment of water before release.
- Limits on chemical use in farming
- Standards for wastewater treatment
- Incentives for soil conservation methods
- Protected areas for forests and wetlands
Innovative Research And Future Trends
New research finds better ways to clean water and stop soil loss. Technology helps monitor and improve conditions.
Scientists develop filters, sensors, and smart farming tools. These tools save water, reduce chemicals, and protect soil.
- Advanced water filtration systems
- Soil moisture sensors for efficient irrigation
- Biodegradable materials to reduce pollution
- Data analysis for better land use planning
Credit: www.txdot.gov
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Methods Of Water Purification?
Water purification methods include filtration, sedimentation, and disinfection. Filtration removes particles and impurities, while sedimentation allows particles to settle. Disinfection kills harmful microorganisms. Advanced methods like reverse osmosis and UV treatment are also used. Each method ensures safe and clean water for consumption and use.
How Does Soil Erosion Affect Water Quality?
Soil erosion leads to sediment in water bodies. This sediment reduces water quality by increasing turbidity. It also carries pollutants like pesticides and fertilizers into water sources. Contaminated water affects aquatic life and human health. Controlling soil erosion is essential for maintaining clean water.
Why Is Controlling Soil Erosion Important?
Controlling soil erosion prevents loss of fertile land. It maintains soil health and agricultural productivity. Erosion control also reduces sedimentation in water bodies. This protects water quality and aquatic ecosystems. Effective erosion control measures include vegetation cover, terracing, and sustainable farming practices.
What Is The Role Of Vegetation In Erosion Control?
Vegetation stabilizes soil and reduces erosion. Plant roots bind soil particles, preventing them from being washed away. Vegetation also slows down water flow, reducing its erosive power. Planting trees and grasses is an effective erosion control strategy. It enhances soil health and supports biodiversity.
Conclusion
Protecting water and soil is key for a healthy planet. Clean water keeps people and animals safe from harm. Controlling soil erosion stops land from losing its nutrients. Both efforts support farming and preserve natural habitats. Small actions by many can make a big difference.
We all depend on water and soil every day. Taking care of them means a better future for everyone. Simple steps today lead to a cleaner, greener world tomorrow. Let’s work together to protect these vital resources.